Tutorial¶
Installation¶
dgm1 requires numpy and gdal.
Using pip¶
pip install dgm1
Using conda¶
dgm1 is not available in conda, but we recommend to install numpy and gdal with conda before installing dgm1 with pip:
conda install numpy
conda install gdal
pip install dgm1
Introduction¶
dgm1 is a package to download and process digital elevation model (dem) data provided by the Government of the
State Nord Rhine-Westphalia in Germany. DGM1 is the German acronym for Digitales Geländemodel with one meter
resolution.
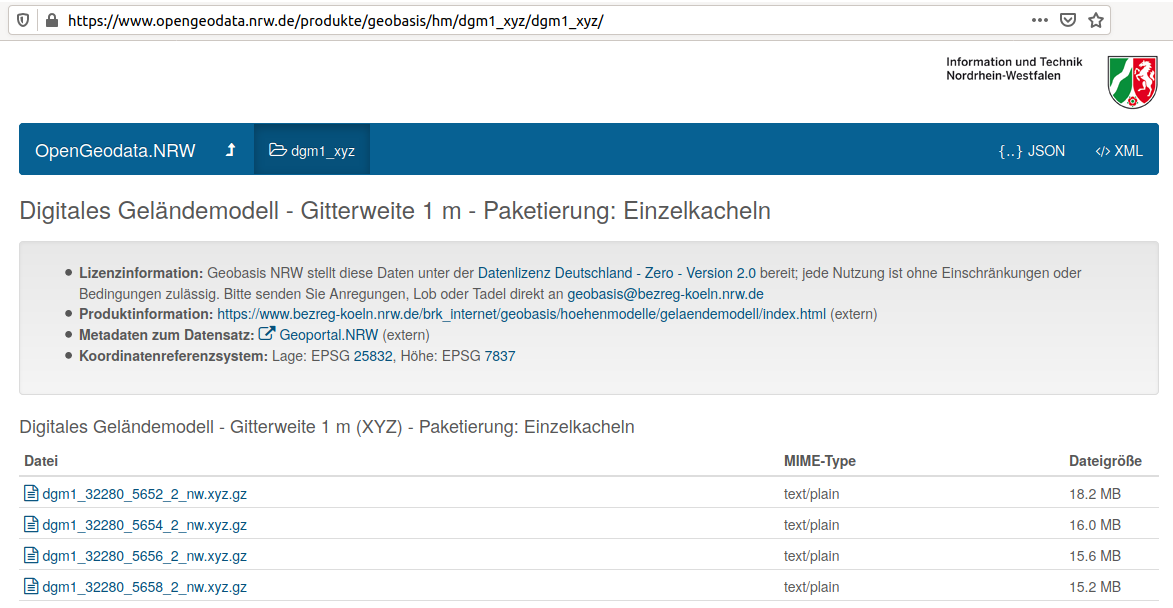
Each xyz.gz file in https://www.opengeodata.nrw.de/produkte/geobasis/hm/dgm1/dgm1_xyz/ contains a list of 4,000,000 tuples (x, y, z) corresponding to a raster of 2000x2000 pixels. The compound coordinate reference system is EPSG 25832 for the horizontal component and EPSG 7837 for the vertical component.
Features¶
download
transform into TIF files
resample
create VRT files (GDAL Virtual Format)
mosaic and clip
Quickstart¶
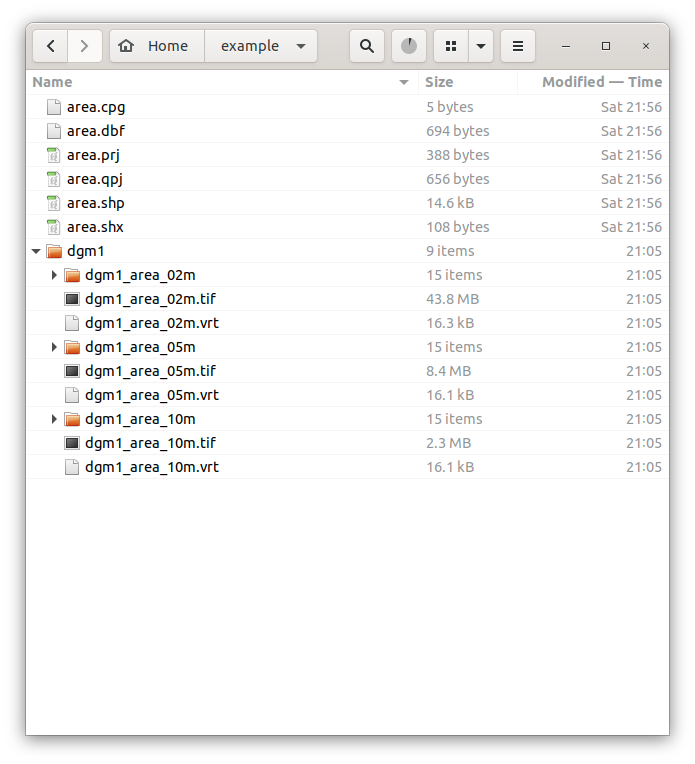
Downloaded data and project data can be save in different directories. In the example below:
~/dgm1: product directory
~/example/: project directory
~ symbolizes home directory, e.g., C:/users/myname/dgm1 and C:/users/myname/example.
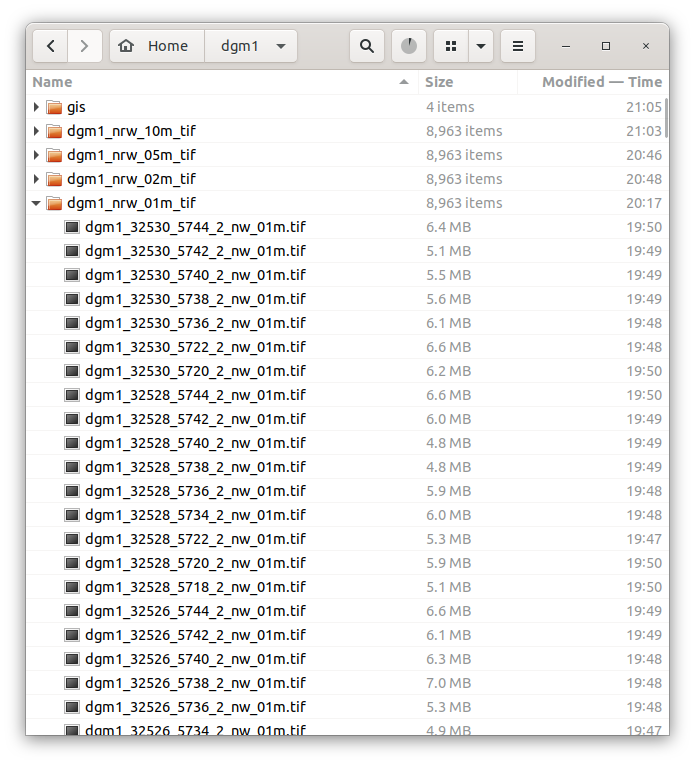
Data is downloaded and processed in the following structure:
~/dgm1/dgm1_nrw_01m_tif/: downloaded data
~/dgm1/dgm1_nrw_02m_tif/: resampled data
~/dgm1/dgm1_nrw_05m_tif/: resampled data
~/dgm1/dgm1_nrw_10m_tif/: resampled data
Note
~/dgm1 and its subdirectories are created automatically.
while ~/dgm1 is user defined, its subdirectories are not.
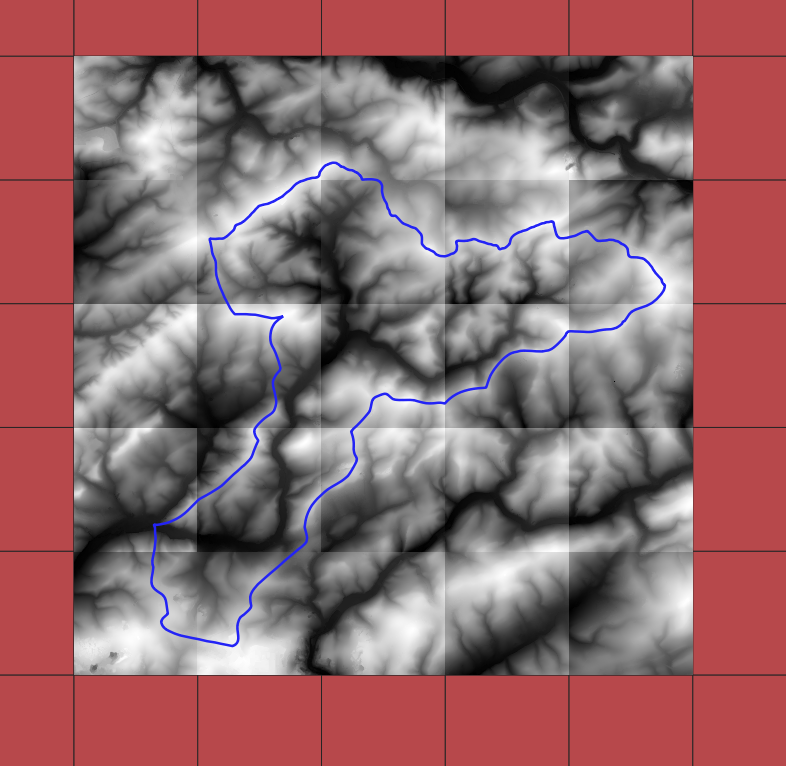
In the code below only rasters intersecting the project area ~/example/area.shp are downloaded.
from dgm.dgm1_nrw import DGM1NRW
# create an instance of the class DGM1NRW
# all ca. 9000 rasters will be downloaded.
# dgm1 = DGM1NRW(dgm1_dir='~/dgm1')
# only intersecting rasters will be downloaded.
dgm1 = DGM1NRW( dgm1_dir='~/dgm1', shp_region='~/example/area.shp')
# create a shapefile with polygons (2x2 km²) representing dem-tiles and save in
# ~/dgm/gis/dgm1_2_nw.shp
dgm1.create_shapefile()
# download all XYZ files intersecting with the region ('~/example/area.shp') and
# save them as TIF files
dgm1.download()
# resample the original 1 meter raster to 2, 5, and 10 meters pixel_size
dgm1.resample(pixel_size=2)
dgm1.resample(pixel_size=5)
dgm1.resample(pixel_size=10)
In the following block VRT files and mosaic are created for the area ~/example/area.shp
# create a GDAL Virtual Format for different resolutions. Each VRT file consists of the file
# `.vrt` and a corresponding directory. For example: file `~/example/dgm1_area_01m.vrt` and
# directory `~/example/dgm1_area_01m`.
dgm1.create_vrt('~/example/dgm1/dgm1_area_01m.vrt', pixel_size=1)
dgm1.create_vrt('~/example/dgm1/dgm1_area_02m.vrt', pixel_size=2)
dgm1.create_vrt('~/example/dgm1/dgm1_area_05m.vrt', pixel_size=5)
dgm1.create_vrt('~/example/dgm1/dgm1_area_10m.vrt', pixel_size=10)
# mosaic TIF files intersecting the region
dgm1.mosaic('~/example/dgm1/dgm1_area_01m.tif', pixel_size=1)
dgm1.mosaic('~/example/dgm1/dgm1_area_02m.tif', pixel_size=2)
dgm1.mosaic('~/example/dgm1/dgm1_area_05m.tif', pixel_size=5)
dgm1.mosaic('~/example/dgm1/dgm1_area_10m.tif', pixel_size=10)
Instance¶
from dgm.dgm1_nrw import DGM1NRW
dgm1 = DGM1NRW(dgm1_dir='D:/dgm1', region='~/example/area.shp')
The class DGM1NRW has one mandatory (dgm1_dir) and one optional (shp_region) parameter:
dgm1_diris the directory of downloaded and processed rasters.shp_regionis an optional shapefile of the region of interest. If given, downloading and processing applies to this region only, otherwise to the whole State NRW (ca. 9000 files).
Download¶
DGM1NRW.download() downloads and unzip server files, transform them from XYZ into TIF format and
save them locally in the folder dgm1_nrw_01m_tif. If shp_region is not defined, all ca. 9000 files will be
download, requiring many hours and ca. 50 GB disk. Otherwise, it downloads DEM files intersecting shp_region.shp only.
n_cores is an optional parameter to allow parallel downloading and processing. If a computer has n cores,
\(1 \leq n\_cores \leq n - 1\). In the example below, the intentionally high \(n\_cores = 40\) will be reduced
to n_cores = 11 if the computer has \(n = 12\) cores. Any high number of cores can be given in order
to use \(n - 1\) cores. If you want to know the number of cores of your computer:
import multiprocessing
print(multiprocessing.cpu_count())
Note
As of April 2020 three out of ca. 90000 raster files were inconsistent:
dgm1_32426_5624_2_nw.xyz.gz
dgm1_32456_5776_2_nw.xyz.gz
dgm1_32442_5770_2_nw.xyz.gz
Downloading inconsistent files:
Downloading 3 files from https://www.opengeodata.nrw.de/produkte/geobasis/hm/dgm1_xyz/dgm1_xyz/ using 3 cores
Filename: dgm1_32456_5776_2_nw.xyz.gz, array.shape = (6000,): cannot reshape array of size 6000 into shape (4000000,3)
Filename: dgm1_32442_5770_2_nw.xyz.gz, array.shape = (6000,): cannot reshape array of size 6000 into shape (4000000,3)
Filename: dgm1_32426_5624_2_nw.xyz.gz, array.shape = (11999988,): cannot reshape array of size 11999988 into shape (4000000,3)
3 files downloaded in 6.35 seconds
Download raster intersecting a region¶
from dgm.dgm1_nrw import DGM1NRW
dgm1 = DGM1NRW('~/dgm1', '~/example/area.shp')
dgm1.download() # n_cores = 1
Download all¶
from dgm.dgm1_nrw import DGM1NRW
dgm1 = DGM1NRW('~/dgm1')
dgm1.download(n_cores=40)
Shapefile¶
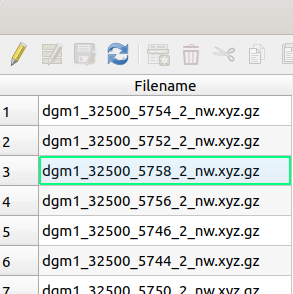
create_shapefile() creates the shapefile gis/dgm1_2_nw.shp in the directory dgm1_dir. The shapefile
contains square corresponding to the DEM files found in
https://www.opengeodata.nrw.de/produkte/geobasis/hm/dgm1_xyz/dgm1_xyz/. It squares from all files found on the server.
The shapefile has an attribute Filename with the raster file name (see Figures below).
from dgm.dgm1_nrw import DGM1NRW
dgm1 = DGM1NRW(dgm1_dir='~/dgm1', region='~/example/area.shp')
dgm1.create_shapefile()
Resample¶
Each downloaded TIF file can be resample to a divisor of 2000 (2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 16, 20, 25, 40, 50, 80, 100, 125, 200, 250, 400, 500, 1000, 2000).
from dgm.dgm1_nrw import DGM1NRW
dgm1 = DGM1NRW('~/dgm1')
dgm1.resample(pixel_size=2) # rasters with 1000x1000 pixels
dgm1.resample(pixel_size=5) # rasters with 400x400 pixels
dgm1.resample(pixel_size=10) # rasters with 200x200 pixels
The class attribute DGM1NRW.compress_options = [‘COMPRESS=LZW’, ‘PREDICTOR=2’] can be modified before
downloading:
from dgm.dgm1_nrw import DGM1NRW
dgm1 = DGM1NRW('~/dgm1')
dgm1.compress_options` = ['COMPRESS=LZMA']
dgm1.download(11)
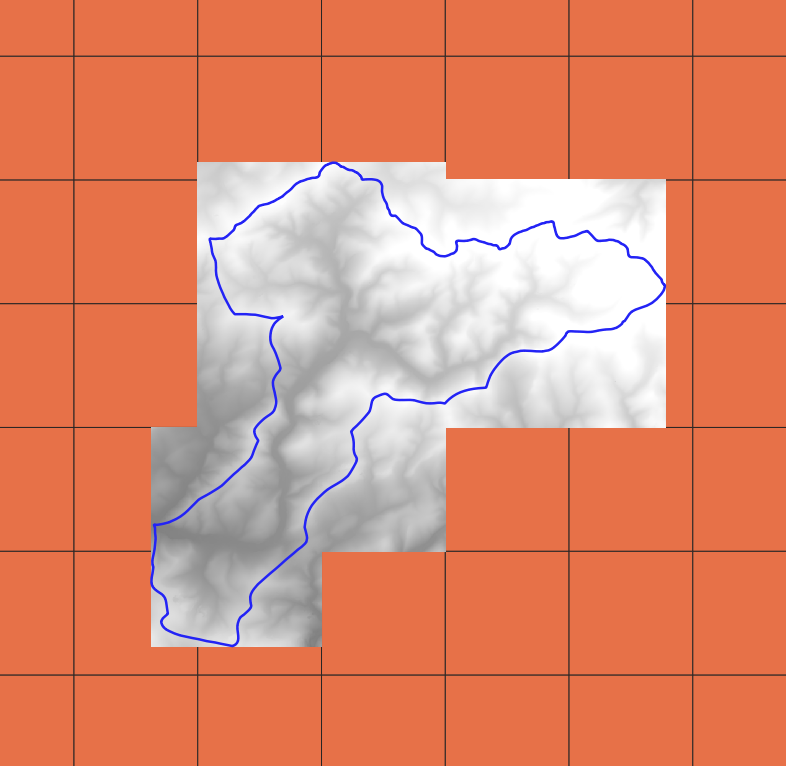
VRT file¶
The GDAL Virtual format creates a kind of mosaic file composed of tiles saved individually and listed in an XML file. Together with the (.vrt) there is a folder with the same name (without the suffix .vrt) containing the corresponding TIF files. It is very useful to create large rasters, which cannot be created or processed otherwise due to computer limitations.
from dgm.dgm1_nrw import DGM1NRW
dgm1 = DGM1NRW('~/dgm1', '~/example/area.shp')
dgm1.create_vrt('~/example/dgm1/dgm1_area_01m.vrt', pixel_size=1)
Mosaic¶
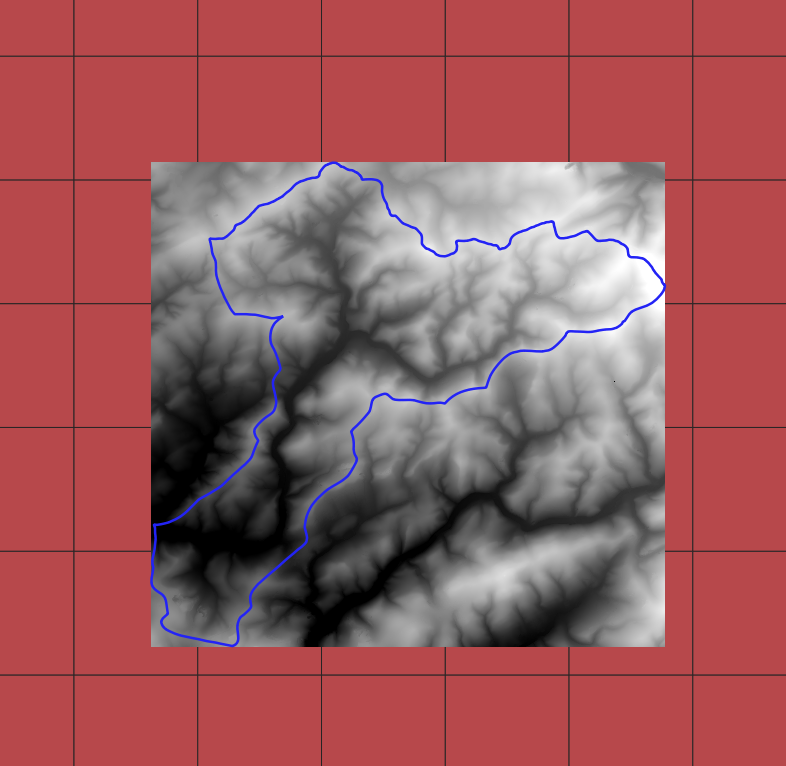
Mosaic will create one raster file (default TIF file) from rasters intersecting the region. There are three types of output raster extent:
clipped to
shp_regionenvelope of
shp_regionenvelope of rasters intersecting
shp_region
from dgm.dgm1_nrw import DGM1NRW
dgm1 = DGM1NRW('~/dgm1', '~/example/area.shp')
dgm1.mosaic('~/example/dgm1/dgm1_area_02m_clip.tif', pixel_size=2, extent='clip')
dgm1.mosaic('~/example/dgm1/dgm1_area_02m_region.tif', pixel_size=2, extent='region')
dgm1.mosaic('~/example/dgm1/dgm1_area_02m_rasters.tif', pixel_size=2, extent='rasters')
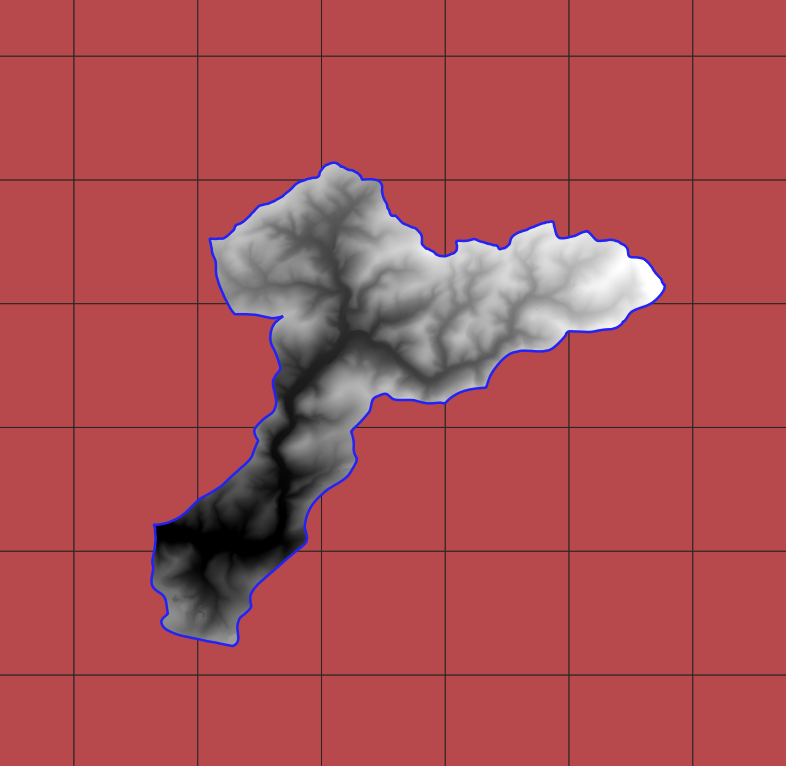

Be aware that your computer may not support the creation of very large files due to RAM size limitations. If the region is large, the resolution (pixel_size) must increase to cope the RAM availability.
Warning
Due to memory limitations, your computer may freeze if you mosaic a very large file at a low resolution!